C Programming Data Types
In C programming, variables or memory locations should be declared before it can be used. Similarly, a function also needs to be declared before use.
Data types simply refers to the type and size of data associated with variables and functions.
OR
A data type specifies the type of data that a variable can store such as integer, floating, character etc.
Data types in C
| Types | Data Types |
|---|---|
| Primary Data Type | integer(int),character(char), floating(float) and void |
| Derived Data Type | array, pointer, structure, union, Enumeration |
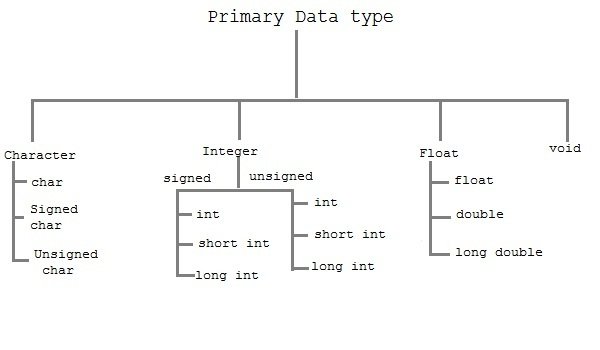
1. Primary Data Types
These are fundamental data types in C namely integer(int), floating(float), character(char) and void.
int - Integer data types
Integers are whole numbers that can have both positive and negative values but no decimal values.
Example: 0, -5, 5, 7, 10
In C programming, keyword int is used for declaring integer variable. For example:
int id;
Here, id is a variable of type integer.
You can declare multiple variable at once in C programming. For example:
int id, age;
The size of int is either 2 bytes(In older PC's) or 4 bytes. If you consider an integer having size of 4 byte( equal to 32 bits), it can take 232 distinct states as: -231,-231+1, ...,-2, -1, 0, 1, 2, ..., 231-2, 231-1
Similarly, int of 2 bytes, it can take 216 distinct states from -215 to 215-1. If you try to store larger number than 231-1, i.e,+2147483647 and smaller number than -231, i.e, -2147483648, program will not run correctly.
float - Floating types
Floating type variables can hold real numbers such as: 2.34, -9.382, 5.0 etc. You can declare a floating point variable in C by using either float or double keyword. For example:
float accountBalance; double bookPrice;
Here, both accountBalance and bookPrice are floating type variables.
In C, floating values can be represented in exponential form as well. For example:
float normalizationFactor = 22.442e2;
Difference between float and double
The size of float (single precision float data type) is 4 bytes. And the size of double (double precision float data type) is 8 bytes. Floating point variables has a precision of 6 digits whereas the precision of double is 14 digits.
char - Character types
Keyword char is used for declaring character type variables. For example:
char test = 'h';
Here, test is a character variable. The value of test is 'h'.
The size of character variable is 1 byte.
void - Void types
void type means no value. This is usually used to specify the type of functions.
2. Derived data types
Data types that are derived from fundamental data types are called derived data types. Derived data types don't create a new data type but, instead they add some functionality to the basic data types. In C, derived data type are : Array, Pointer, Structures, Enumeration & Union.
C Qualifiers
Qualifiers alters the meaning of base data types to yield a new data type.
Size qualifiers
Size qualifiers alters the size of a basic type. There are two size qualifiers, long and short. For example:
long double i;
The size of double is 8 bytes. However, when long keyword is used, that variable becomes 10 bytes.
C Program to Demonstrate the Working of Keyword long
The long is a size modifier, indicated by keyword long, that may increase the size of a variable during declaration. This program will demonstrate the working of long keyword.
Example: Program to Demonstrate the Working of long
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a;
long b;
long long c;
double e;
long double f;
printf("Size of int = %ld bytes \n", sizeof(a));
printf("Size of long = %ld bytes\n", sizeof(b));
printf("Size of long long = %ld bytes\n", sizeof(c));
printf("Size of double = %ld bytes\n", sizeof(e));
printf("Size of long double = %ld bytes\n", sizeof(f));
return 0;
}
Output
Size of int = 4 bytes Size of long = 8 bytes Size of long long = 8 bytes Size of double = 8 bytes Size of long double = 16 bytes
In this program, the sizeof operator is used to find the size of int, long, long long, double and long double.
The long keyword cannot be used with float and char type variables.
There is another keyword short which can be used if you previously know the value of a variable will always be a small number.
Sign qualifiers
Integers and floating point variables can hold both negative and positive values. However, if a variable needs to hold positive value only, unsigned data types are used. For example:
// unsigned variables cannot hold negative value unsigned int positiveInteger;
There is another qualifier signed which can hold both negative and positive only. However, it is not necessary to define variable signed since a variable is signed by default.
An integer variable of 4 bytes can hold data from -231 to 231-1. However, if the variable is defined as unsigned, it can hold data from 0 to 232-1.
It is important to note that, sign qualifiers can be applied to int and char types only.
Constant qualifiers
An identifier can be declared as a constant. To do so const keyword is used.
const int cost = 20;
The value of cost cannot be changed in the program.
Volatile qualifiers
A variable should be declared volatile whenever its value can be changed by some external sources outside the program. Keyword volatile is used for creating volatile variables.
MIND IT !
The primary data types are integer-based and floating-point based. C language supports both signed and unsigned literals.
The memory size of primary data types may change according to 32 or 64 bit operating system.
Let's see the primary data types. Its size is given according to 32 bit architecture.
| Data Types | Memory Size | Range |
|---|---|---|
| char | 1 byte | ?128 to 127 |
| signed char | 1 byte | ?128 to 127 |
| unsigned char | 1 byte | 0 to 255 |
| short | 2 byte | ?32,768 to 32,767 |
| signed short | 2 byte | ?32,768 to 32,767 |
| unsigned short | 2 byte | 0 to 65,535 |
| int | 2 byte | ?32,768 to 32,767 |
| signed int | 2 byte | ?32,768 to 32,767 |
| unsigned int | 2 byte | 0 to 65,535 |
| short int | 2 byte | ?32,768 to 32,767 |
| signed short int | 2 byte | ?32,768 to 32,767 |
| unsigned short int | 2 byte | 0 to 65,535 |
| long int | 4 byte | -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 |
| signed long int | 4 byte | -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647 |
| unsigned long int | 4 byte | 0 to 4,294,967,295 |
| float | 4 byte | |
| double | 8 byte | |
| long double | 10 byte |
LearnFrenzy provides you lots of fully solved "C Programming Data Types" Questions and Answers with explanation.