C Programming Functions
A function is a group of statements that together perform a specific task. Every C program has at least one function, which is main().

Why use function ?
Function are used for divide a large code into module, due to this we can easily debug and maintain the code. For example if we write a calculator programs at that time we can write every logic in a separate function (For addition sum(), for subtraction sub()). Any function can be called many times.
Advantage of Function
- Code Re-usability
- Develop an application in module format.
- Easily to debug the program.
- Code optimization: No need to write lot of code.
Types of functions in C programming
Depending on whether a function is defined by the user or already included in C compilers, there are two types of functions in C programming
There are two types of functions in C programming:
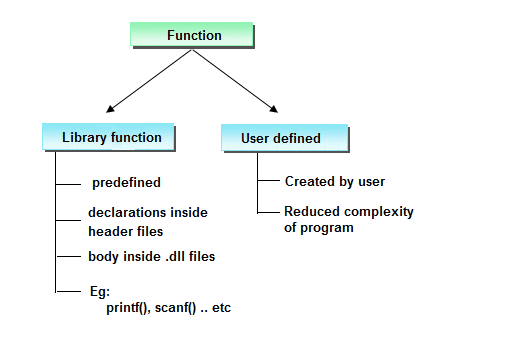
Standard library functions
The standard library functions are built-in functions in C programming to handle tasks such as mathematical computations, I/O processing, string handling etc.
These functions are defined in the header file. When you include the header file, these functions are available for use. For example:
The printf() is a standard library function to send formatted output to the screen (display output on the screen). This function is defined in "stdio.h" header file.
There are other numerous library functions defined under "stdio.h", such as scanf(), fprintf(), getchar() etc. Once you include "stdio.h" in your program, all these functions are available for use.
Limitations of Library function
- All predefined function are contained limited task only that is for what purpose function is designed for same purpose it should be used.
- As a programmer we do not having any controls on predefined function implementation part is there in machine readable format.
- In implementation whenever a predefined function is not supporting user requirement then go for user defined function.
User-defined functions
These functions are created by programmer according to their requirement for example suppose you want to create a function for add two number then you create a function with name sum() this type of function is called user defined function.
Defining a function
Defining of function is nothing but give body of function that means write logic inside function body.
Syntax
return_type function_name(parameter)
{
function body;
}
MIND IT !
- Return type: A function may return a value. The return_type is the data type of the value the function returns.Return type parameters and returns statement are optional.
- Function name: Function name is the name of function it is decided by programmer or you.
- Parameters: This is a value which is pass in function at the time of calling of function A parameter is like a placeholder. It is optional.
- Function body: Function body is the collection of statements.
Function Declarations
A function declaration is the process of tells the compiler about a function name. The actual body of the function can be defined separately.
return_type function_name(parameter);
Note: At the time of function declaration function must be terminated with ;.
calling a function
When we call any function control goes to function body and execute entire code. For call any function just write name of function and if any parameter is required then pass parameter.
Syntax
function_name();
or
variable=function_name(argument);
Note: At the time of function calling function must be terminated with ';'.
Example of Function
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void sum(); // declaring a function
clrsct();
int a=10,b=20, c;
void sum() // defining function
{
c=a+b;
printf("Sum: %d", c);
}
void main()
{
sum(); // calling function
}
Output
Sum: 30
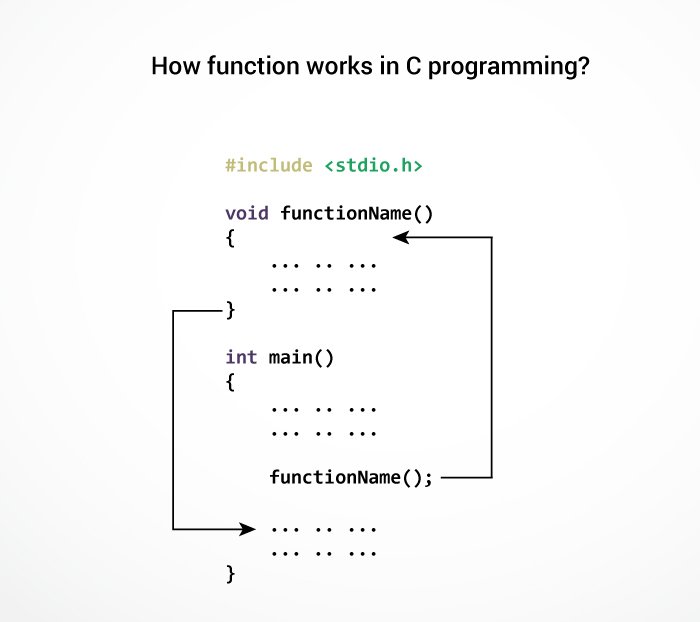
How user-defined function works?
#include <stdio.h>
void functionName()
{
... .. ...
... .. ...
}
int main()
{
... .. ...
... .. ...
functionName();
... .. ...
... .. ...
}
The execution of a C program begins from the main() function.
When the compiler encounters functionName(); inside the main function, control of the program jumps to
void functionName()And, the compiler starts executing the codes inside the user-defined function.
The control of the program jumps to statement next to functionName(); once all the codes inside the function definition are executed.
Remember, function name is an identifier and should be unique.
Advantages of user-defined function
1. The program will be easier to understand, maintain and debug.
2. Reusable codes that can be used in other programs
3. A large program can be divided into smaller modules. Hence, a large project can be divided among many programmers.
