Biology
Here we have given some important facts of Biology. We hope it will help you to know about biology and to score more marks in General science.
GK Science: Some facts about Biology
- Length of Alimentary Canal Approximately- 8 metres.
- BMR (Basal Metabolic Rate) – 1600 K. Cal / day.
- Number of Cells in Body 75 trillion
- Longest Bone Femur (Thigh bone).
- Weight of Brain : 1400 gms
- Blood Volume 6.8 litres (in 70 kg body)
- Normal B.P 120 / 80 mm Hg
- Number of R.B.C (a) In Male : 4.5 – 5.0 million / cubic mm.(b) In Female : 4.0 – 4.5 million / cubic mm
- Life Span of R.B.C : 120 days
- Normal W.B.C Count 5000 – 1000 / cubic mm
- Life Span of W.B.C : 3 – 4 days
- L.C. (Differential Leucocyte Count)
- (a) Basophils : 0.5 – 1%
- (b) Eosinophils : 1 – 3%
- (c) Monocytes : 3 – 8%
- (d)Neutrophils : 40 – 70%
- (e) Lymphocytes : 2 – 25%
- Blood Platelets Count : 2,00,000 – 4,00,000 / cubic mm
- Haemoglobin (a) In Male : 14 – 15.6 gm / 100 c.c. of blood(b)In Female : 11 – 14 gm / 100 c.c. of blood
- Hb Content in Body 500 – 700 gm
- Universal Blood Donor: O Rh -ve
- Universal Blood Recipient : AB
- Blood Clotting Time: 2 – 5 minutes
- Average Body Weight: 70 kg
- Normal Body Temperature : 98.4° F or 37° C
- Breathing Rate : 16 – 20 / minute
- Dental Formula Adult : 2123 / 2123 = 32;
- Child : 22 Milk Teeth
- Largest Endocrine Gland : Thyroid
- Gestation Period 9 months (253 – 266 days)
- Normal Heart Beat” 72 – 75 / minute
- Largest Gland : Liver
- Largest Muscle in the Body Gluteus maximus (Buttock Muscle)
- Largest Artery: Abdominal Aorta
- Largest Vein: Inferior Venacava
- Largest W.B.C : Monocyte
- Smallest W.B.C : Lymphocyte
- Longest Nerve : Sciatic
- Longest Cell : Neuron (Nerve Cell)
- Menstrual Cycle : 28 days
- Menopause Age : 45 – 50 Years
- Minimum Distance for proper vision : 25 cm
- Pulse Rate 72 / minute.
- Normal Sperm Count 200 – 350 million / ejaculation.
- FSR (normal Erythrocyte Sedimentation rate) 4 – 10 min / hr
- pH of Gastric Juice : 1.4
- pH of Urine : 6.0
- pH of Blood: 7.35 – 7.45
- pH of Bile : 7.5
- pH of Pancreatic Juice : 8.5
- Total Number of Muscles in the Body: 639
- Total Number of Bones in the Body : 206
- Largest Organ of Human Body: Skin
GK Science: Facts About Animal Cell
- Robert Hook was the first to coin the term ‘Cell’
- Cell is defined as structural and functional unit of the body
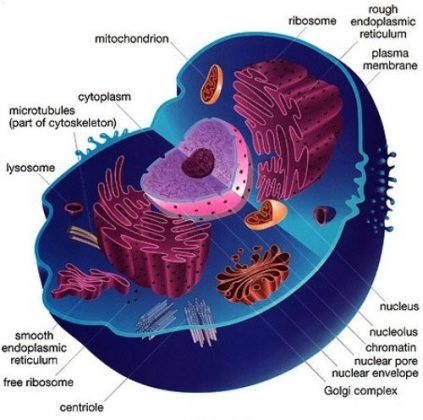
PROTOPLASM
- It is the living substance of the cell. It is a viscous, colourless fluid and is the seat for all physiological functions.
ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM
- The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of membranes found throughout the cell and connected to the nucleus. The membranes are slightly different from cell to cell and a cell’s function determines the size and structure of the ER
RIBOSOMES
- They are the smallest organelles of the cell
- Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis in the cell
GLOGI COMPLEX (DICTYOSOMES)
- The main function of Golgi complex is cell secretion e. it packs and transports certain materials like proteins and polysaccharides out of the cells.
- It is involved in the formation of primary lysosmes
MITOCHONDRIA
- Mitochondrion are called ‘power house of the cell’.
PLASTIDS
The plastids are of three types :-
1. Leucoplast
2. Chromoplast
3. Chloroplast
- Leucoplasts are colourless plastids, found in the underground parts of plants which are not exposed of light.
- Chromoplasts are orange, yellow or red coloured plastids found in petals, fruits and roots in certain higher plants. The red colour of ripe tomatoes is the result of Chromoplasts which contain the red pigment lycopene
- Chloroplasts are the most important and most common plastids found in all the photosynthesising cells except prokaryotes. Blue-green algae however, lacks chloroplasts
LYSOSOMES : are also called suicidal bags as when these are injured by a toxic substance, the enzymes thus released can digest the whole cell.
LearnFrenzy provides you lots of fully solved "Biology" Questions and Answers with explanation.
