You’re probably aware that JavaScript is the programming language most often used to add interactivity to the front end of a website, but its capabilities go far beyond that—entire sites can be built on JavaScript, extending it from the front to the back end, seamlessly.
Express.js and Node.js gave JavaScript newfound back-end functionality—allowing developers to build software with JavaScript on the server side for the first time. Together, they make it possible to build an entire site with JavaScript: You can develop server-side applications with Node.js and then publish those Node.js apps as websites with Express.
Because Node.js itself wasn’t intended to build websites, the Express framework is able to layer in built-in structure and functions needed to actually build a site. It’s a pretty lightweight framework that’s great for giving developers extra, built-in web application features and the Express API without overriding the already robust, feature-packed Node.js platform. In short, Express and Node are changing the way developers build websites.
EXPRESS.JS FRAMEWORK BASICS
Express builds:
i. Single-page, multi-page, and hybrid mobile and web apps
ii. Common back-end functions for web applications
iii. APIs (application programming interfaces)
Templating engines : Express comes with two templating engines, Jade and EJS, which facilitate the flow of data into a website structure.
MVC pattern : Express supports the Model-View-Controller architecture, a really helpful way to build websites in a model-driven format.
Platform : Node.js
Operating system : It’s cross-platform, so it’s not limited to one OS.
The Express Generator lets you create complex applications quickly.
How Express.js works
Here is a block scheme on how Express.js works with Node.js and MongoDB
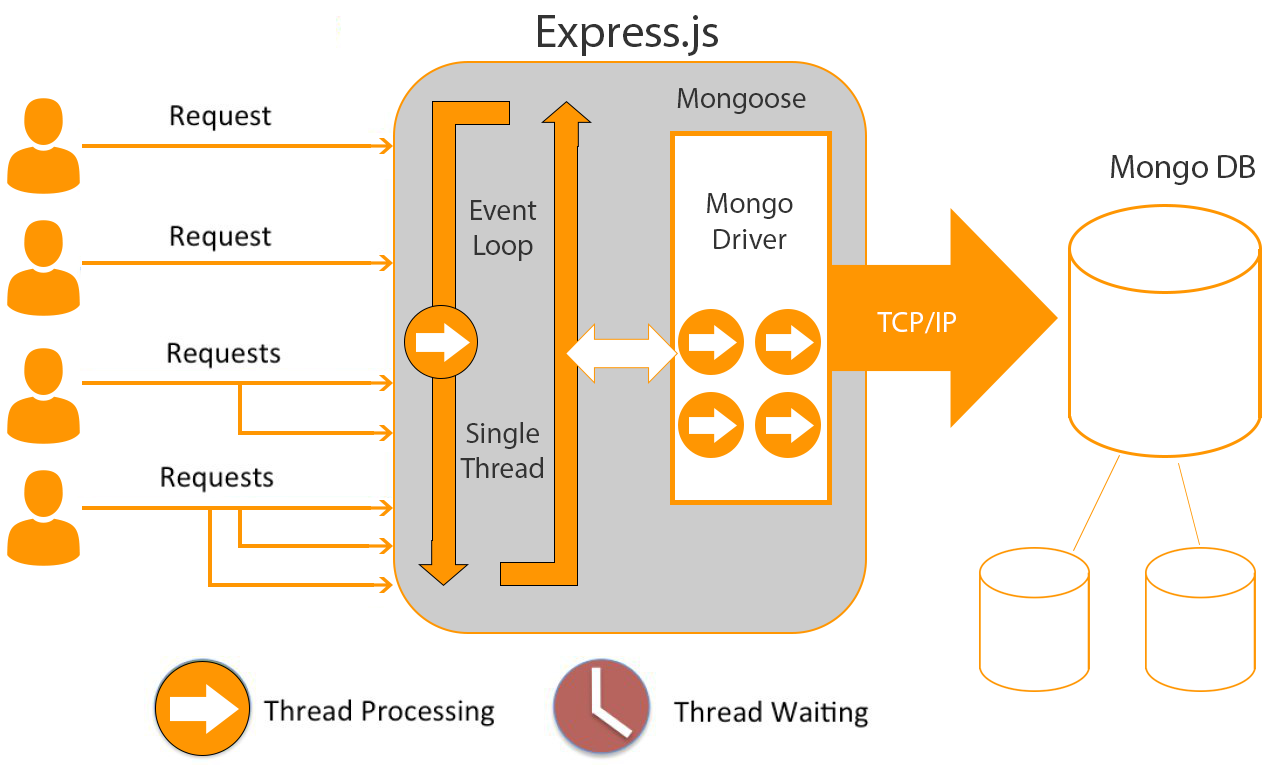
Node.js is an event-driven server, that has a single thread which manages all connections to the server. It processes all the requests in the callbacks without delaying their flow.
As you can see from the picture above, when the request enters the server, Express processes it into the callback without blocking the main stack.
Imagine that you need to retrieve some data from the file or database. Such process may be time-consuming (for example because of disc read delay). The average server will block all other requests until these data are delivered.
Node JS, in its turn, registers the logic of data post-processing in the callback. Data are processed in parallel, so the server can accept another data at the same time. As the result, Node.js can process the bigger amount of requests more efficiently.
Mongoose is the Mongo driver add-in, that perfectly fits the Express ecosystem. The main advantage of MongoDB is that it is JavaScript oriented. It means that the driver transfers all the data they are without wasting time on adjusting them to the programming environment. MongoDB is developed for scale-out data-driven servers.
Each request in MongoDB is processed in the same way as in the callback. It means that the server doesn't have to wait (block the stock) until the certain data are transferred and can process other requests simultaneously. It is extremely important because the scale-out database can be situated on one or several physically remote servers, so retrieving data from them is time-sapping.
Now let’s conclude the whole process once again. Server receives the request and registers the event data processing. Then the event sends the request to the remote Mongo server. After this is done, some time is needed for data to return. Simultaneously, the server is processing other requests. When the data arrives, Mongo driver invokes the user request handler. The user request handler delivers the data back to the client.
This blog provides Frequently asked Top 25+ Express.Js interview questions and best answers for freshers and 2-4 year experienced developers.
1. What is Express Js? What are core features of Express framework?
Express JS is a framework which helps to develop web and mobile applications. Its works on node.js plateform. Its sub part of node.js.
Express JS Features:
Following are some of the core features of Express framework ?
2. What type of web application can built using Express JS?
you can build single-page, multi-page, and hybrid web applications.
3. What are core features of Express framework?
4. Why I should use Express JS?
Express 3.x is a light-weight web application framework to help organize your web application into an MVC architecture on the server side.
5. How to get variables in Express.js in GET Method?
var express = require('express');
var app = express();
app.get('/', function(req, res){
/* req have all the values **/
res.send('id: ' + req.query.id);
});
app.listen(3000);
6. How to get POST a query in Express.js?
var bodyParser = require('body-parser')
app.use( bodyParser.json() ); // to support JSON-encoded
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({ // to support URL-encoded
extended: true
}));
7. How to output pretty html in Express.js?
app.set('view options', { pretty: true });8. How to get the full url in Express?
var port = req.app.settings.port || cfg.port;
res.locals.requested_url = req.protocol + '://' + req.host + ( port == 80 || port == 443 ? '' : ':'+port ) + req.path;
9. How to remove debugging from an Express app?
var io = require('socket.io').listen(app, { log: false });
io.set('log level', 1);10. How to download a file?
app.get('/download', function(req, res){
var file = __dirname + '/download-folder/file.txt';
res.download(file);
});11. How to 404 errors?
app.get('*', function(req, res){
res.send('what???', 404);
});12. What is the parameter "next" used for in Express?
app.get('/userdetails/:id?', function(req, res, next){
});Note: req and res which represent the request and response objects
nextIt passes control to the next matching route.
13. What Function Arguments Are Available To Express.js Route Handlers?
The arguments available to an Express.js route handler function are:
req - the request object
res - the response object
next (optional) - a function to pass control to one of the subsequent route handlers
The third argument may be omitted, but is useful in cases where you have a chain of handlers and you would like to pass control to one of the subsequent route handlers, and skip the current one.
14. How To Config Properties In Express Application?
In an ExpressJS Application, we can config properties in following two ways:
With Process.ENV:
- Create a file with name ‘.env’ inside the project folder.
- Add all the properties in ‘.env’ file.
- In server.js any of the properties can be used as:
var host = process.env.APP_HOST app.set('host', host); logger.info('Express server listening on http://' + app.get('host'));
With RequireJs:
- Create a file called ‘config.json’ inside a folder called ‘config’ inside the project folder.
- Add config properties in config.json.
{ "env":"development", "apiurl":"http://localhost:9080/api/v1/" }
Use require to access the config.json file.
var config = require('./config/config.json');15. How To Allow Cors In Expressjs? Explain With An Example?
In order to allow CORS in Express.js, add the following code in server.js:
app.all('*', function(req, res, next) {
res.set('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', '*');
res.set('Access-Control-Allow-Methods', 'GET, POST, DELETE, PUT');
res.set('Access-Control-Allow-Headers', 'X-Requested-With, Content-Type');
if ('OPTIONS' == req.method) return res.send(200);
next();
});
16. How To Redirect 404 Errors To A Page In Expressjs?
In server.js add the following code to redirect 404 errors back to a page in our ExpressJS App:
/* Define fallback route */
app.use(function(req, res, next) {
res.status(404).json({errorCode: 404, errorMsg: "route not found"});
});
17. Explain Error Handling In Express.js Using An Example?
From Express 4.0 Error handling is much easier. The steps are as following:
Create an express.js application and as there is no built-in middleware like errorhandler in express 4.0, therefore, the middleware need to be either installed or need to create a custom one.
Create a Middleware:
Create a middleware as following:
// error handler
app.use(function(err, req, res, next) {
// set locals, only providing error in development
res.locals.message = err.message;
res.locals.error = req.app.get('env') === 'development' ? err : {};
// render the error page
res.status(err.status || 500);
res.render('error');
});Install Error Handler Middleware:
Install errorhandler.
npm install errorhandler --save
Create a variable.
var errorhandler = require('errorhandler')
Use the middleware as following:
if (process.env.NODE_ENV === 'development') {
// only use in development
app.use(errorhandler({log: errorNotification}))
}
function errorNotification(err, str, req) {
var title = 'Error in ' + req.method + ' ' + req.url
notifier.notify({
title: title,
message: str
})
}
18. How To Enable Debugging In Express App?
In different Operating Systems, we have following commands:
On Linux the command would be as follows:
$ DEBUG=express:* node index.js
On Windows the command would be:
set DEBUG=express:* & node index.js
19. How To Implement Jwt Authentication In Express App ? Explain With Example?
- Create a folder called ‘keys’ inside project folder.
- Install some dependencies as following:
- Npm install jsonwebtoken –save
- Add the login router routes/index.js
router.post('/login, function(req, res) {
// find the user
User.findOne({
name: req.body.username
}, function(err, res) {
if (err) throw err;
if (!res) {
res.json({ success: false, message: Login failed.' });
} else if (res) {
// check if password matches
if (res.password != req.body.password) {
res.json({ success: false, message: Login failed. Wrong password.' });
} else {
var token = jwt.sign(res, app.get('superSecret'), {
expiresInMinutes: 1600
});
// return the information including token as JSON
res.json({
success: true,
message: 'Valid token!',
token: token
});
}
} });
});Use the token in application
jwt = require("express-jwt");
app.use(function(req, res, next) {
var token = req.body.token || req.query.token || req.headers['x-access-token'];
if (token) {
jwt.verify(token, app.get('superSecret'), function(err, decoded) {
if (err) {
return res.json({ success: false, message: 'Invalid token.' });
} else {
req.decoded = decoded;
next();
}
});
} else {
return res.status(403).send({
success: false,
message: 'No token given.'
});
}
});20. How Should I Structure My Application?
There is no definitive answer to this question. The answer depends on the scale of your application and the team that is involved. To be as flexible as possible, Express makes no assumptions in terms of structure.
Routes and other application-specific logic can live in as many files as you wish, in any directory structure you prefer. View the following examples for inspiration:
- Route listings
- Route map
- MVC style controllers
Also, there are third-party extensions for Express, which simplify some of these patterns:
- Resourceful routing
21. How Do I Define Models?
Express has no notion of a database. This concept is left up to third-party Node modules, allowing you to interface with nearly any database.
22. How Can I Authenticate Users?
Authentication is another opinionated area that Express does not venture into. You may use any authentication scheme you wish.
23. Which Template Engines Does Express Support?
Express supports any template engine that conforms with the (path, locals, callback) signature.
24. How Do I Render Plain Html?
There’s no need to “render” HTML with the res.render() function. If you have a specific file, use the res.sendFile() function. If you are serving many assets from a directory, use the express.static() middleware function.
25. Types of apps, where Node.js+Express.js is the right choice
As we already mentioned, Node.js can handle a large amount of simultaneous connections, so it will be useful for server-side applications interacting with third-party resources and gathering data from them.
Node.js is a great choice for building the back-end of applications for tracking website visitors and visualizing the outcoming data. For example, you need to investigate reviews about your company as soon as they appear, keep track of all ratings and analyze them. JSSolutions has developed such project for gathering reviews from different websites in one application. We decided to build it with Node.js exactly because of the reasons, mentioned above.
Node.js allows to easily build applications that are updated in real time. Who decided to develop a real time polls application that will display voting results, updating in real time. He has chosen this technology because of its simple architecture and scalability. In addition, Node.js is an event-based and non-blocking driven server that can handle a large number of real-time users.


Comments (4)
What others are saying about this article
Sujith Rao
ReaderRahul Singh
Readerpiccosoft
ReaderJhanvi Mehta
ReaderLeave a Comment
Share your thoughts and join the discussion